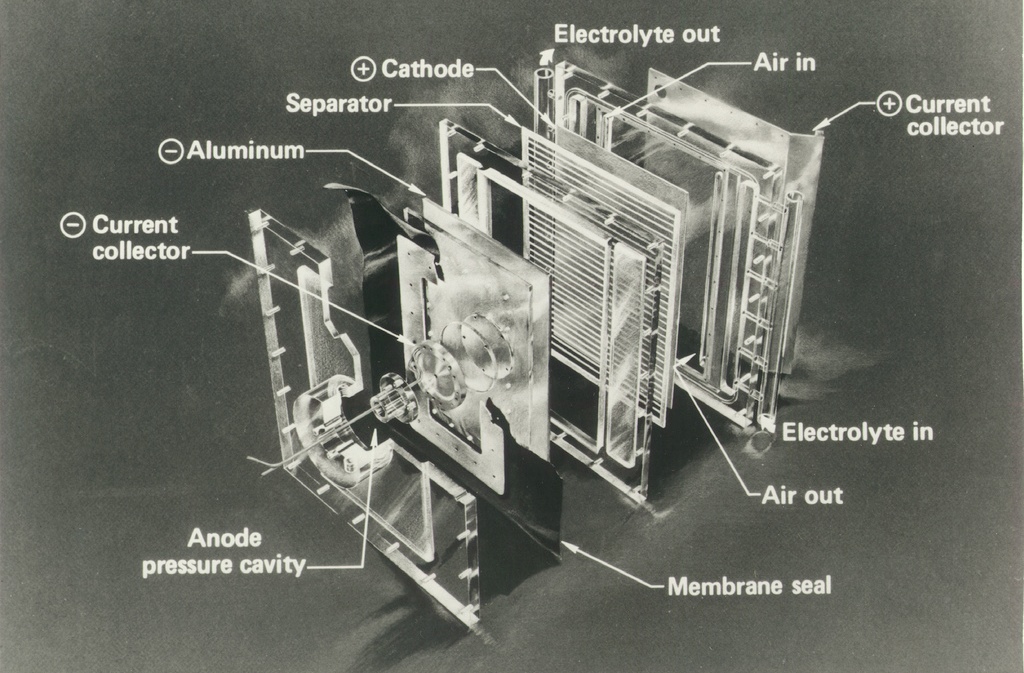
The chemical reaction of the aluminum-air battery is similar to that of the zinc-air battery. The aluminum-air battery uses high-purity aluminum Al (containing 99.99% aluminum) as the negative electrode, oxygen as the positive electrode, and potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH) aqueous solution as the electrolyte. . Aluminum absorbs oxygen in the air, and a chemical reaction occurs when the battery is discharged, and the aluminum and oxygen are converted into aluminum oxide.
Will Aluminum Air Batteries Replace Lithium Batteries?
At present, aluminum batteries that can replace lithium batteries are still in the trial production stage and have not been put into commercial use. So in general, whether aluminum-air batteries will replace lithium batteries is still unknown, so let’s take a look at the problems that aluminum-air batteries will encounter when replacing lithium batteries.
In terms of battery cruising range, aluminum-air batteries are indeed a breakthrough compared to lithium batteries. However, due to the corrosion of the anode during the discharge process of the aluminum-air battery, hydrogen will be generated, which will not only lead to the loss of the anode material, but also increase the internal loss of the battery; in addition, the aluminum-air battery consumes aluminum, which is required when the battery life ends. Reinstalling aluminum, etc., has greatly hindered the commercialization of aluminum-air batteries. And in terms of vehicle applications, aluminum-air batteries are still unknown, and they are not even comparable to hydrogen fuel cells.
Analysis of the reasons why aluminum-air batteries cannot replace lithium batteries
1. Mostly used for emergency power supply
“The aluminum-air battery is not a battery used to store electrical energy multiple times in the traditional sense, but a chemical reaction device that releases electrical energy.” Chen Tao said that its working principle is the process of the oxidation reaction of active metals in water to release energy— – Through the electrolyte and special electrode materials, the released energy is output in the form of electrical energy.
In layman’s terms, for aluminum-air batteries, the active metal is aluminum, similar to zinc-air batteries, magnesium-air batteries, etc., but according to the activity of the metal (the severity of the oxidation reaction in water or air) , the electrolyte and other auxiliary materials used are slightly different.
“‘Just add clean water’ is only in the life cycle of the battery, and the substance consumed is aluminum, not water.” Chen Tao told reporters that during the working process of the battery, it continuously outputs electrical energy, metal aluminum It is also continuously oxidized and consumed to generate aluminum hydroxide, and the production of electricity is conditioned on the consumption of aluminum containing chemical energy. “The 100-kilogram aluminum-air battery stores enough power to travel 3,000 kilometers.” After driving 3,000 kilometers, the battery’s life is over, and it needs to be reinstalled, that is, to replenish metal aluminum.
According to reports, aluminum-air batteries have been introduced as early as the 1960s. But until now, most of its research is still in the theoretical stage, and there are not many practical applications. In China, most of its research focuses on emergency power supply; in foreign countries, scientists are either studying certain electrode materials, or studying battery systems for special applications, and are trying to seek breakthroughs in the application technology of aluminum-air batteries.
2. Security risks to be tested
“Inconvenience of use is the biggest bottleneck of aluminum-air batteries at present.” Chen Tao believes that in addition to the inconvenience of using batteries that store electrical energy, compared with other gas-based fuel cells, there are also many inconveniences, such as hydrogen fuel cells, which can easily add hydrogen to hydrogen. Note, storage, and transportation to chemical reaction devices, but it is obviously inconvenient for aluminum as a metal solid. Secondly, there are many side reactions, the reaction process is not easy to control, and some reaction products hinder the reaction to a certain extent, release a lot of heat, and generate flammable and explosive gases at the same time.
Aluminum appears to be playing a bigger role in the development of electric vehicles. An interesting phenomenon is that the battery life of Tesla electric vehicles in the United States can be increased to 300 kilometers to 400 kilometers. The batteries used are mainly nickel-cobalt-aluminum ternary materials, while my country’s electric vehicles use nickel-cobalt-manganese. The difference between the metals is aluminum.
“The aluminum material used in Tesla is mainly used in batteries that can store electrical energy multiple times. Its function is to improve the energy density of the battery. The battery of the same weight can store more electrical energy and make the car’s driving range longer. Long.” Chen Tao believes that from this point of view alone, it is indeed a breakthrough. However, the resulting security risks need to be further tested in practice.
Electric vehicles powered by lithium-ion batteries are difficult to popularize. The biggest obstacle is the limited driving range. The current range is mostly between 135 kilometers and 480 kilometers. Unless there are a large number of fast charging stations along the way, it is not suitable to drive electric vehicles for long-distance travel. A few vehicles with a distance of more than 200 kilometers are particularly expensive and cannot be popularized.
3. Car is still unknown
Can aluminum-air batteries replace lithium-ion batteries? Geely Automobile Research Institute has done relevant simulation modeling experiments to study the application of aluminum-air batteries as on-board energy for electric vehicles from the perspective of vehicle dynamics, focusing on the amount of electricity and power that can be released by itself.
“From the experimental results, the aluminum-air battery is more suitable as a backup battery for battery life.” Du Zhiqiang said that the aluminum-air battery is an energy source. Compared with the battery that can store electrical energy, the aluminum-air battery of the same weight can release the electrical energy. More, its energy density is high, but its releasable power is extremely low, and it does not meet the needs of vehicles when used alone, especially when it is just starting. It’s the equivalent of a petrol car with a big tank but a small engine that can go a long way, but very slowly. In contrast, the speed of lithium-ion batteries will be more stable. If an aluminum-air battery with the same power (that is, the vehicle has the same speed) is used, its weight will be about 4 to 5 times that of a lithium-ion battery.
That is to say, the standard energy of an electric vehicle should be, in actual use, take the advantage of the aluminum-air battery to obtain a longer driving mileage, and at the same time make up for the shortcoming of the aluminum-air battery, with a power-type battery, The vehicle has a good dynamic performance.
“For vehicle applications, aluminum-air batteries are still unknown.” Du Zhiqiang believes that there are currently some applications of aluminum-air batteries in mobile communication devices and notebook computers, but they are all experimental and not very widespread. In the future application in the field of electric vehicles, there are still many technical problems that need to be solved urgently. Whether it can successfully become the on-board energy of electric vehicles depends on the final choice of the market. In other fields, judging from the technical characteristics of the aluminum-air battery itself, it seems more suitable as an emergency power source and a mobile power station.
From the current selection of Geely’s electric vehicle batteries, it is basically the same as the industry. Du Zhiqiang said, “I personally think that the future development direction is to add fuel cells on the basis of existing batteries to form a hybrid vehicle power supply of ‘fuel cell + battery’. In terms of fuel cell selection, hydrogen fuel cells are superior to aluminum-air batteries. such as metal fuel cells.”